The Stream Transport Model in the Internet Refers to
Opportunistic TLS Transport Layer Security refers to extensions in plain text communication protocols which offer a way to upgrade a plain text connection to an encrypted TLS or SSL connection instead of using a separate port for encrypted communicationSeveral protocols use a command named STARTTLS for this purposeIt is a form of opportunistic encryption and is. OSI uses the network layer to define routing standards and protocols.
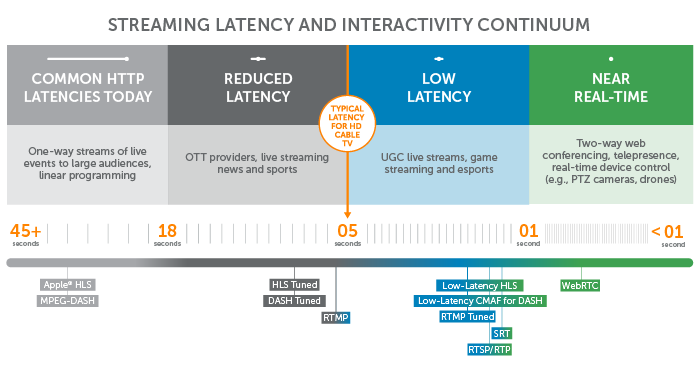
Streaming Protocols Everything You Need To Know Wowza
The Transport layer in the OSI model as well as TCPIP model provides statistical multiplexing of several application layer data flows tofrom the same computer.

. Code-division multiplexing CDM is a technique in which each channel transmits its bits as a coded channel-specific sequence of pulses. The pattern repeats after every fourth packet see Figure 4. It provides the hardware means of sending and receiving data on a carrier including defining cables cards and physical aspects.
The second transport protocol specified for use with AVB-capable networks is IEEE Std 1733-2011. Sample clock encoding in AVTP IEEE Std 1722. Internet of Things IoT and Cyber Physical Systems CPS have emerged as the dominant technological revolution which has offered a connected.
TCP refers to Transmission Control Protocol. The data in this layer is represented as a stream of bits. OSI Model Layer 1 or the physical layer conveys the bit streamelectrical impulse light or radio signalthrough the network at the electrical and mechanical level.
OSI refers to Open Systems Interconnection. OSI model use two separate layers physical and data link to define the functionality of the bottom. For transmission the bits must be encoded into signals.
The Physical layer of the OSI model is responsible for the following functions. OSI follows a vertical approach. This coded transmission typically is accomplished by transmitting a.
TCPIP follows a horizontal approach. It specifies the type of encoding or how. TCPIP uses only the Internet layer.
This means that the timestamp refers to a differently numbered sample in each packet and results in the fourth packet carrying no valid timestamp at all.

Transport Stream An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

How Do Streams Transport And Deposit Sediments
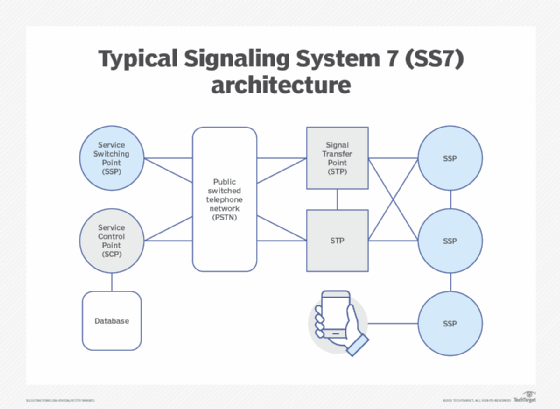
What Is The Stream Control Transmission Protocol Sctp And How Does It Work
No comments for "The Stream Transport Model in the Internet Refers to"
Post a Comment